

The total, 11 electrons, fills orbitals from low energy to higher energy.Īllyl Radical In CH 2CHCH 2, 5 of the carbon 2sp 2 hybrid orbitals combine with the 5 hydrogen 1s orbitals to form 5 C-H bonding orbitals and 5 C-H antibonding orbitals. The nitrogen atom is less electronegative than the oxygen atoms so its atomic orbitals are a little higher in energy.īecause one of the non-bonding orbitals is localized on the N atom, it is a little higher in energy than the four non-bonding orbitals localized on the two oxygen atoms.īecause there is one 2p x orbital on each atom available for pi bonding, there are three pi symmetry molecular orbitals.Įach oxygen atom contributes is 6 valence electrons and the nitrogen contributes 5 electrons. Because of this, the highest energy orbital that is occupied by electrons, the 2 orbital, has only one electron.Īt right are the molecular orbitals for nitrogen dioxide. Nitrogen dioxide has one fewer electron than ozone.
MOLECULAR ORBITAL DIAGRAM OF O2 FULL
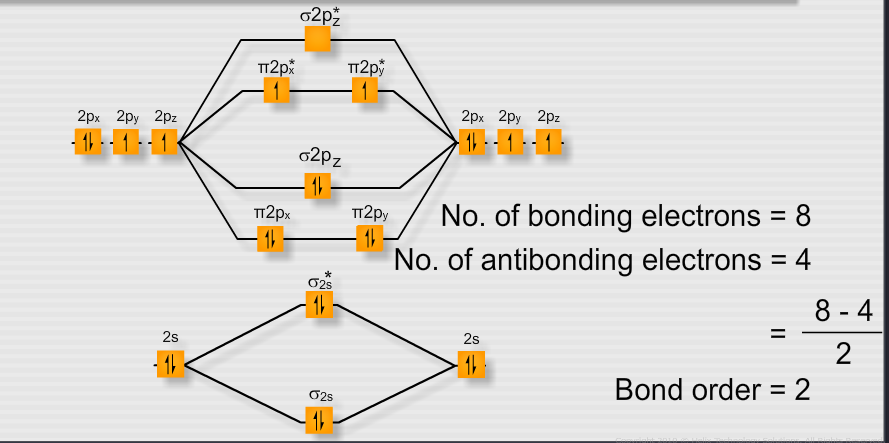
The full molecular orbital diagram with the electrons is below. 3, antibonding, the mathematical sign of the wavefunction changes with every atom, repulsive interaction between atoms.2, non-bonding, zero pi electron density on the second atom.1, bonding all the way across the 3 atoms.The p orbitals in the picture above indicate electron density in those orbitals. The 2p x orbital on O 1, the 2p x orbital on O 2, and 2p x orbital on O 3 combine to form three pi symmetry orbitals. Two 2sp 2 orbitals on O 1, one 2sp 2 orbital on O 2, and two 2sp 2 orbitals on O 3 are non-bonding.O 3 uses one 2sp 2 orbital to combine with a second 2sp 2 orbital of O 2, making another sigma bonding and sigma antibonding orbital.O 1 uses one 2sp 2 orbital to combine with one 2p 2 orbital of O 2, making a sigma bonding and sigma antibonding orbital.Each oxygen atom combines its 2s, 2p z and 2p y orbitals to make three 2sp 2 hybrid orbitals. We'll use the hybrid orbital approximation. Let's look at the molecular orbital diagram of ozone. If you want #"O"_2^(+)#, take one electron out of the #pi_(2p_y)^"*"# orbital.Pi Bonds over 3 Atoms Pi Bonds over 3 Atoms Lastly, #"N"_2# would have the #sigma_(2p_z)# above the #pi_(2p_x)# and #pi_(2p_y)#, whereas #"O"_2# would have it below. Two #2p_z# orbitals combine to give a #sigma_(2p_z)# bonding and #sigma_(2p_z)^"*"# antibonding MO.These are the same energy as the #pi_(2p_x)# counterparts. Two #2p_y# orbitals combine to give a #pi_(2p_y)# bonding and #pi_(2p_y)^"*"# antibonding orbital.These are the same energy as the #pi_(2p_y)# counterparts. Two #2p_x# orbitals combine to give a #pi_(2p_x)# bonding and #pi_(2p_x)^"*"# antibonding orbital.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
